Final Exam
True or False (1 point each)
- In a distributed version control system with an optimistic locking/merging model, when one develper checks out a file no other developers may edit the file.
- In a centralized version control system with a pessimistic locking/merging model, when one developer checks out a file no other developers may edit the file.
- The path of a Java source file from the source root must match the package name of the Java file.
.jarfiles contain archives of directory trees that contain.classfiles and other files.- In agile software development, detailed system design is done at the beginning of the project.
- Agile software development emphasizes comprehensive documentation, processes, and tools.
- Using CS terms in a variable name is a good idea.
- It’s poor coding practice to, as a rule, comment every function and variable.
- Javadocs for public APIs are useful.
- In general, the fewer the function parameters the better.
- Functions that return error codes make programs clearer by mixing error-handling logic with the main logic of the program.
- Functions should return values rather than update output parameters.
- You should avoid side-effects in your functions.
- In test driven development, you may not begin writing production code until you have written a failing unit test.
- A Junit test method should only have one assert statement.
- Junit test methods are executed in a definite order so that test methods may depend on other test methods.
- You should always use object-oriented class designs rather than data structure-oriented classes.
- According to the Law of Demeter, a class’s public API should not expose its internal structure.
- According to the Single Responsibility Principle, a class should have one reason to change.
- Clean class design usually results in several small classes instead of a few large classes.
Multiple Choice (2 points each)
- A Java classpath specification can contain:
- A. directories in which to find
.classfiles on the filesystem - B.
.jarfiles that contain archives of directory trees that contain.classfiles. - C. all of the above
- D. none of the above
- A. directories in which to find
- Which of the following is a best (not just legal) directory path to contain a class named
foo.bar.Baz?- A.
src/foo - B.
src/bar/foo - C.
src/main/java/foo/bar - D. All of the above are correct.
- A.
- Agile software development processes minimize risk by
- A. hiring only the best software engineers.
- B. doing the higher-risk tasks in the last iteration.
- C. doing the higher-risk tasks first in each iteration.
- The benefits of build automation include
- A. repeatable builds.
- B. documentation of build process.
- C. All of the above.
- Which of the following guidelines apply to clean names in programs?
- A. All variable names should be short.
- B. All variable names should be long.
- C. The length of a variable name should be proportional to its scope.
- D. None of the above.
- The stepdown rule (a.k.a. newspaper metaphor) in writing functions means placing
- A. longer functions before shorter functions.
- B. shorter functions before longer functions.
- C. higher-level functions above helper functions that implement the details.
- D. harder to understand functions before easier to understand functions.
- Which of the following are good formatting practices?
- A. Vertical openness between concepts.
- B. Placing spaces on either side of assignment operators.
- C. Following the team’s rules even if they differ from your own.
- D. All of the above.
- Class size is measured in
- A. lines of code.
- B. number of methods.
- C. number of responsibilities.
- Which of the following are indications of a class’s number of responsibilities?
- A. The number of interfaces it implements.
- B. The vagueness of the class name.
- C. The number of words in the class name.
- D. All of the above.
- Which of the following is a good strategy for cleaning up
switchstatements?- A. Replacing them with
if-elsestatements. - B. Using
Strings for the switch variable. - C. Replacing them with polymorphic classes.
- D. Including
defaultclauses.
- A. Replacing them with
Short Answer (5 points each)
-
Give a case where a comment is helpful.
-
What is the most important consideration in writing a function?
-
Tests should be F.I.R.S.T. Explain each F.I.R.S.T. rule with one sentence or phrase.
-
Write a unit test method for the static method
public static int abs(int n)injava.lang.Math, which returns the absolute value of an integern. Assumejava.lang.Mathhas been imported. Include an assert for each equivalence partition.
Refactoring/Code Cleaning (5 points each)
Apply the principles of clean code to rewrite these code snippets the spaces below them. If the code is in Java, write your solution in Java. If the code is in Scala, write your solution in Scala. If the code is valid in both Java and Scala, write your solution in Scala.
1.
public class Part {
private String m_dsc; // The textual description
public void set(String s) {
m_dsc = s;
}
}
2.
// returns 1 if the file named by s exists, 0 otherwise.
public int file(String s)
3.
// Check to see if the employee is eligible for full benefits
if ((employee.flags & HOURLY_FLAG) && (employee.age > 65))
4.
def mean(xs: Seq[Double]): Double =
if (xs.isEmpty)
throw new ArithmeticException("mean of empty list undefined")
else
xs.sum / xs.length
Design Analysis 1 (5 points each)
Given the following two designs for representing geometric shapes:
Design A:
public class Rectangle {
public Point topLeft;
public double height;
public double width;
}
public class Circle {
public Point center;
public double radius;
}
public class Geometry {
public double area(Object shape) throws NoSuchShapeException {
if (shape instanceof Rectangle) {
Rectangle r = (Rectangle)shape;
return r.height * r.width;
}
else if (shape instanceof Circle) {
Circle c = (Circle)shape;
return Math.PI * c.radius * c.radius;
}
throw new NoSuchShapeException();
}
}
Design B:
public interface Shape {
public double area();
}
public class Rectangle implements Shape {
private Point topLeft;
private double height;
private double width;
public double area() { return height * width; }
}
public class Circle implements Shape {
private Point center;
private double radius;
public double area() { return Math.PI * radius * radius; }
}
-
Give an advantage of Design A.
-
Give an advantage of Design B.
Design Analysis 2 (5 points each)
Given:
public class RealBillingService {
public Receipt chargeOrder(PizzaOrder order, CreditCard creditCard) {
PaypalCreditCardProcessor processor = new PaypalCreditCardProcessor();
// Card charging code ...
}
}
-
List any “smells” in the design or the code.
-
State any principles or design patterns you would use to refactor the code.
-
Write an updated version of the code which applies the principles or design patterns in the previous question. You may need to write additional classes or interfaces. Only write code that is necessary to show the design, that is, dont’ write detailed implementations for methods.
Design Implementation (10 points)
Given the following UML class diagram, write a stubbed out SalariedEmployee class in Scala using Scala idioms. Complete the constructor (if you need one) but don’t give the code inside the curly braces of other methods. Do not include anything you don’t need in this class.
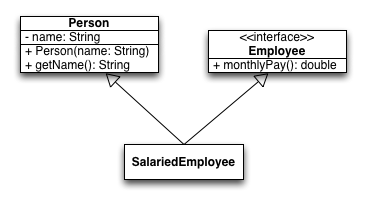
Algebraic Data Types (30 points)
Given the following polymorphic class hierarchy:
trait Feline {
def dinner: Food
}
final class Lion() extends Feline {
def dinner: Food =
Antelope
}
final class Tiger() extends Feline {
def dinner: Food =
TigerFood
}
final class Panther() extends Feline {
def dinner: Food =
Licorice
}
final class Cat(val favouriteFood: String) extends Feline {
def dinner: Food =
CatFood(favouriteFood)
}
Rewrite these classes as an algebraic data type such that you don’t intend ever to add another subclass of Feline. Also write the Food classes as an algebraic data type.